Archives
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-07
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2018-07
-
We tested this hypothesis with two experiments In the
2021-10-12
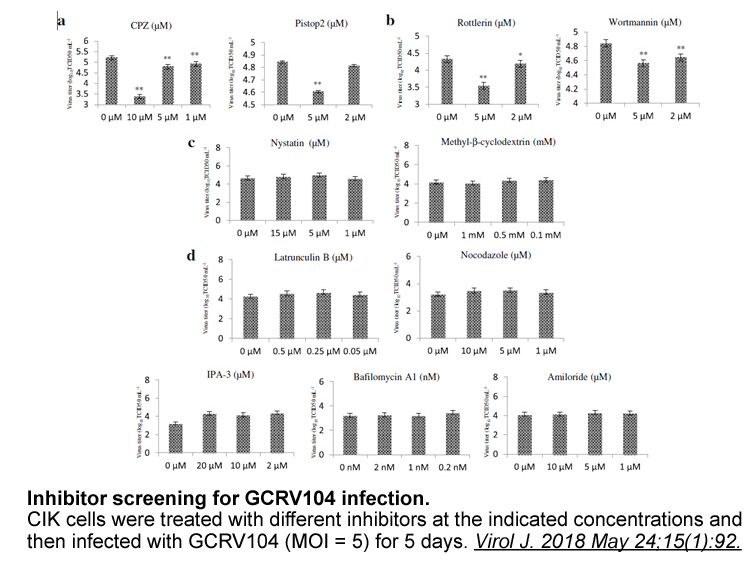
We tested this hypothesis with two experiments. In the first experiment OVX monkeys implanted with an E2 GSK256066 (this results in LH levels similar to the level during the follicular phase) were treated with daily injections of letrozole for 1 week and then EB was injected systemically mimicking t
-
br Reactive Dicarbonyls and Mitochondrial Dysfunction Althou
2021-10-12

Reactive Dicarbonyls and Mitochondrial Dysfunction Although mitochondrial dysfunction has been suggested to be one of the main pathogenic mechanisms in diabetic neuropathy, little is known about the nature and extent of mitochondrial damage resulting from chronic hyperglycemia. Mitochondria funct
-
Next we investigated the accumulation of H
2021-10-12
Next, we investigated the accumulation of [3H]-ribavirin in fresh villous fragments of human placenta, which provide a physiologically relevant, well-described and validated model for assessing drug interactions with ENTs [32], [35], [69], [70]. The uptake of [3H]-ribavirin was time-dependent and si
-
Kern et al observed an
2021-10-12
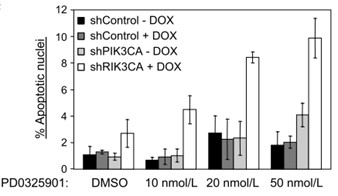
Kern et al observed an overall improvement in behaviors typical for autism during TR. They used the Childhood Autism Rating Score (CARS), to determine the intensity of the change and found lower CARS values after 3 (t(21) = 2.73, p for the children to take part in educational activities facilitated
-
Recent data from an investigation conducted
2021-10-12
Recent data from an investigation conducted with beta-cell cultures and animals suggest that FFAR1 gene depsipeptide sale is modulated by stimulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARG) [10]. Intriguingly, in 2001 we had demonstrated effects of the PPARG Pro12Ala single nucl
-
We have previously shown in the same time
2021-10-11
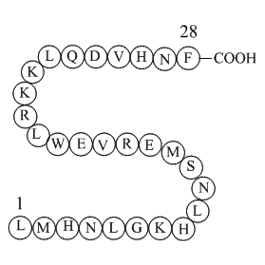
We have previously shown in the same time frame reported here (10 min) that AG was not degraded into DAG [29] and that the half-life of AG in human serum is ∼10 min [49]. However, we cannot rule out in this study that there is not breakdown to DAG that could contribute to the levels of 125I-ghrelin
-
br Some Gardos channel perplexities While much is known abou
2021-10-11
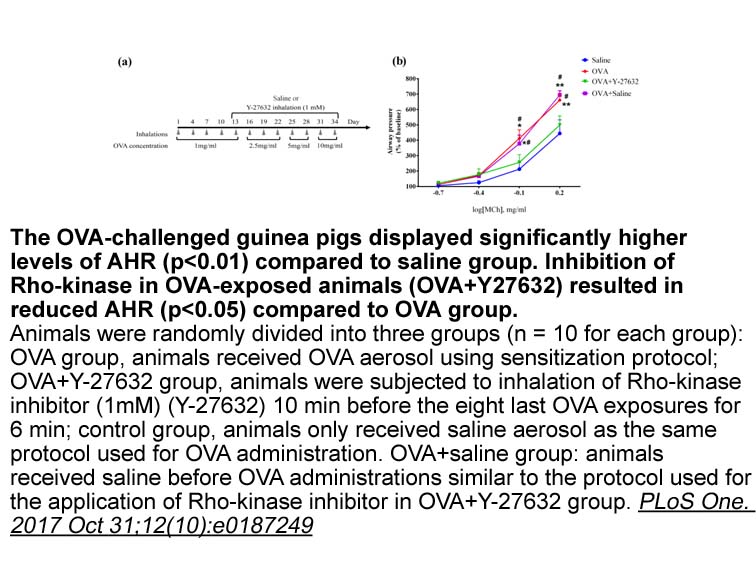
Some Gardos channel perplexities While much is known about the Gardos channel (inside Ca2+-activated K+ channel) and it's characteristics in human red blood Ketorolac tromethamine salt mg (e.g. [18,19]), there are a number of intriguing and unexplained phenomena that are in much need of study.
-
lumiracoxib The observed increase in macroscopic conductance
2021-10-11
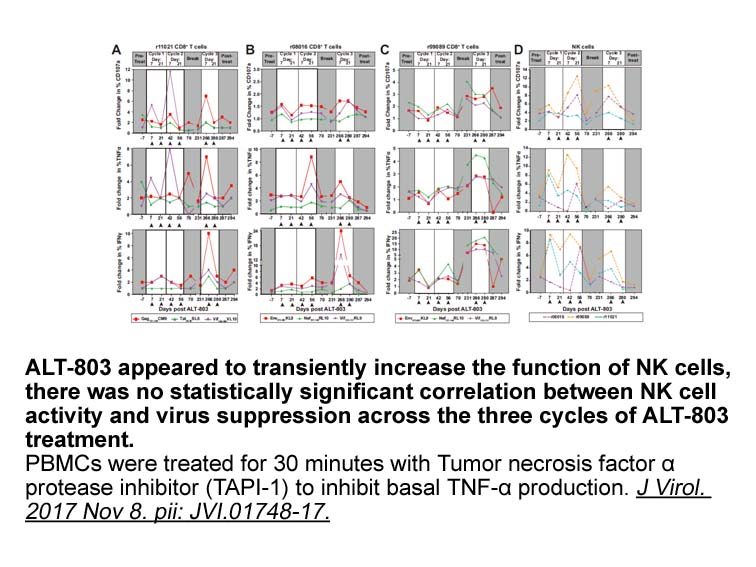
The observed increase in macroscopic conductance could be due to a left shift in the open state probability vs. voltage curve for the high-activity state causing an increase in the open state probability at all potentials. However, an increase of the apparent single channel conductance cannot be ent
-
Further we examined the degradation of Cx
2021-10-11
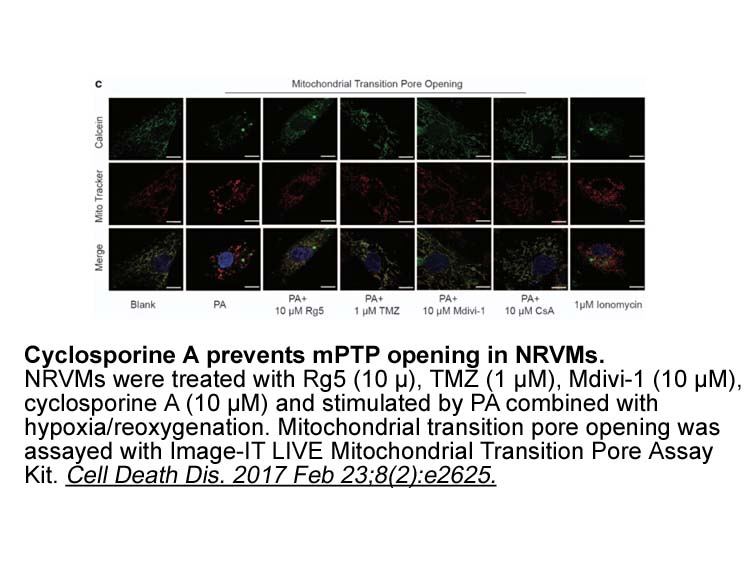
Further, we examined the degradation of Cx43. Autophagy and the proteasome system have previously been implicated in Cx43 degradation (Falk et al., 2014). DEX inhibited communication between anderson kpt by promoting the degradation of Cx43 through autophagy in osteocytes (Gao et al., 2016). In our
-
It is well known that TNF plays a pivotal
2021-10-11
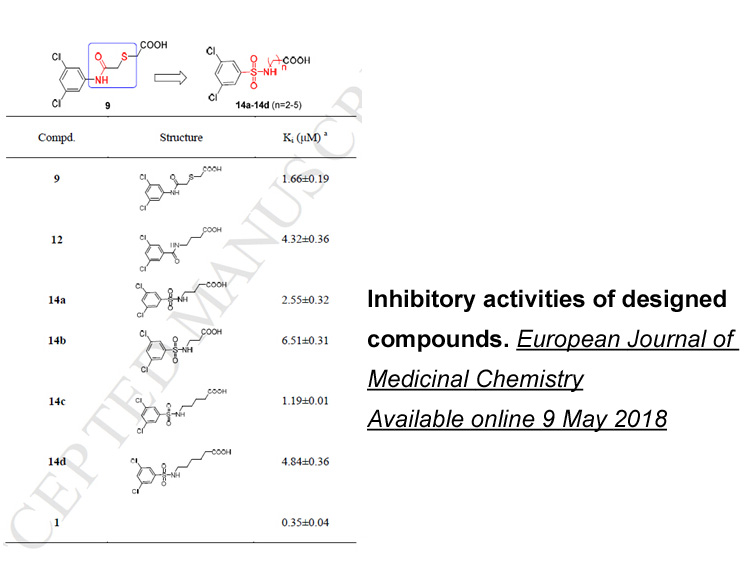
It is well known that TNF-α plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of RA. TNF-α influences diverse pathologic processes including joint destruction as well as inflammatory responses [16]. While TNF-α significantly increases the levels of sFas and mFas expression from FLS, IL-1β and IL-17 have mini
-
Garcinol On the other hand G a GLP could
2021-10-11
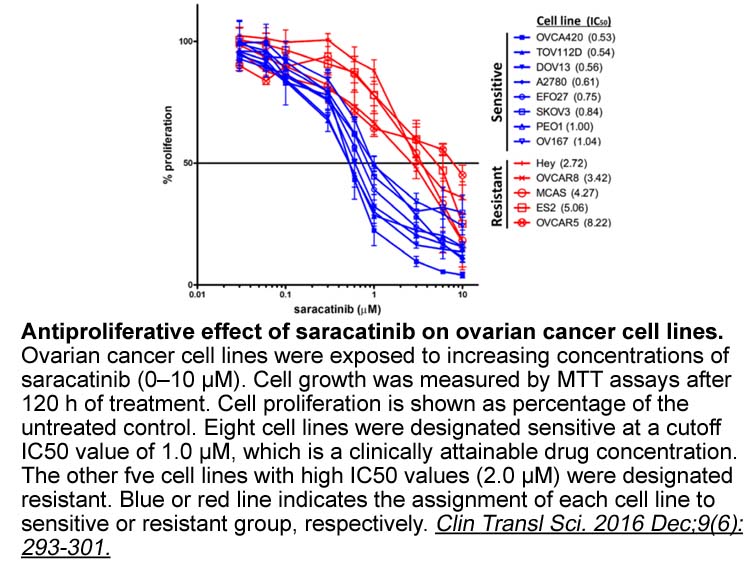
On the other hand, G9a/GLP could also alter neuronal function without directly altering the transcription level of particular plasticity-related protein: the consolidation of early-LTP to late-LTP, as well as the reversal of mGluR-LTD by G9a/GLP inhibition required PKMζ translation and its downstrea
-
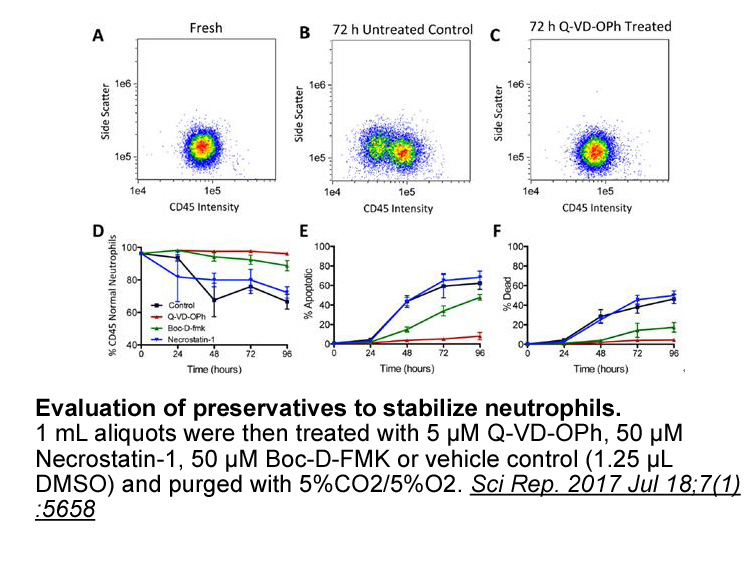
To identify genes with significant expression differences we
2021-10-11
To identify genes with significant 486 2 differences, we performed differential gene expression analysis between the two individuals with TRRAP variants (combined as biological replicates) and two unaffected controls. Gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis of these genes with the GOrilla web applica
-
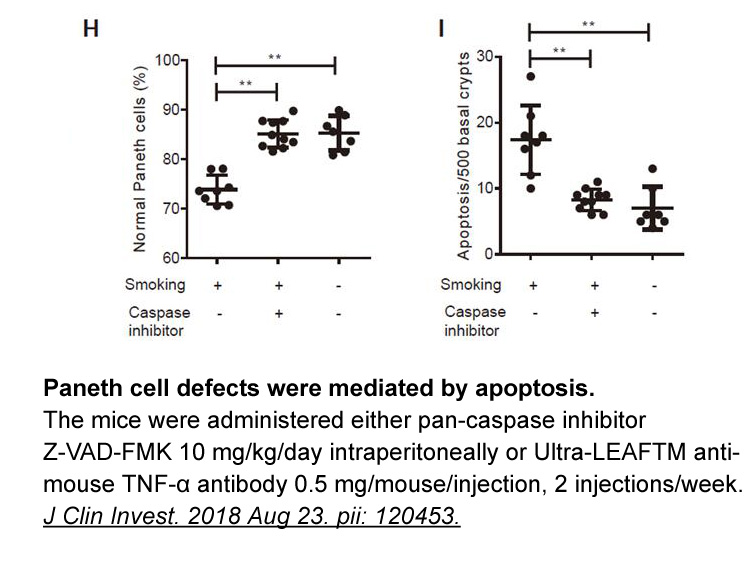
br Epigenetic regulation of OA
2021-10-11
Epigenetic regulation of OA pathogenesis Although epigenome of each cell is unique but can undergo temporal and spatial changes in response to environmental stimuli such as diet, exercise, smoking and disease status. Aberrant epigenetic modifications due to environmental factors are associated wi
-
br Competing interests br Funding
2021-10-11
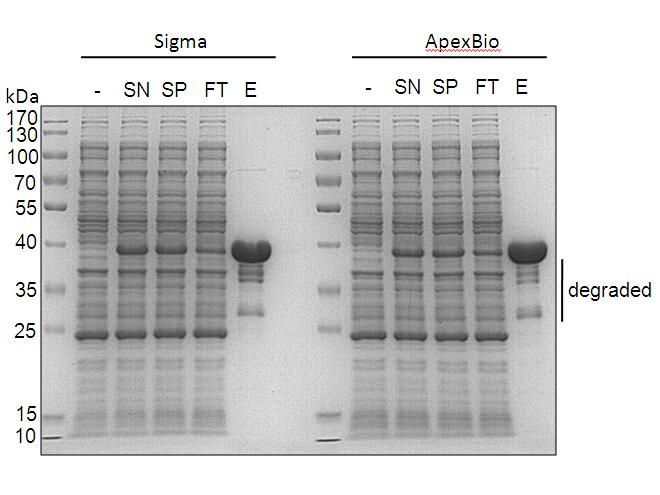
Competing interests Funding Ethical approval Acknowledgement Introduction Hepatitis C is a disease that infects the liver through transmission of the hepatitis C virus (HCV). Because the symptoms of this infection are not pronounced, the infected individuals may not even be aware of t
-
Excessive extracellular glutamate may induce excitotoxic neu
2021-10-11
Excessive extracellular glutamate may induce excitotoxic neuronal damage in disorders of the CNS (Schwartz et al., 2003). EAATs are considered to contribute to prevention of excitotoxicity by glutamate uptake. Our data revealed that expression levels of membrane EAAT proteins in astrocytes are much
15358 records 604/1024 page Previous Next First page 上5页 601602603604605 下5页 Last page